If the frequency of an electromagnetic wave is 6.0, we embark on a scientific odyssey that unravels the intricate tapestry of the electromagnetic spectrum. This exploration delves into the fundamental concepts of frequency, wavelength, and energy, unveiling their profound relationship and diverse applications.
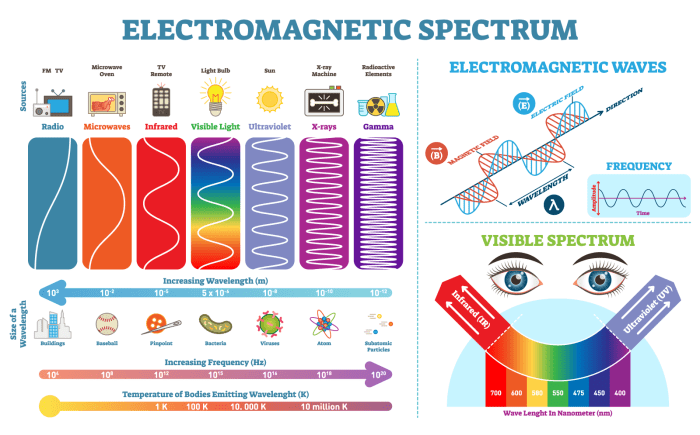
The electromagnetic spectrum, a vast expanse of frequencies, encompasses a myriad of wave types, each possessing unique properties and practical applications. From the ethereal whispers of radio waves to the penetrating power of gamma rays, the spectrum paints a vibrant canvas of electromagnetic phenomena.
Frequency of Electromagnetic Waves
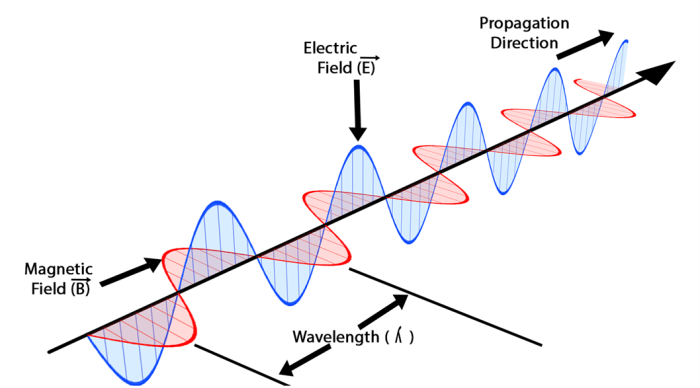
Frequency is a fundamental property of electromagnetic waves that describes the number of oscillations or cycles per unit time. It is measured in Hertz (Hz), which represents one oscillation per second.
The frequency of an electromagnetic wave is inversely proportional to its wavelength, meaning that as frequency increases, wavelength decreases. The relationship between frequency (f), wavelength (λ), and the speed of light (c) is given by the equation: f = c / λ.
Electromagnetic Spectrum, If the frequency of an electromagnetic wave is 6.0
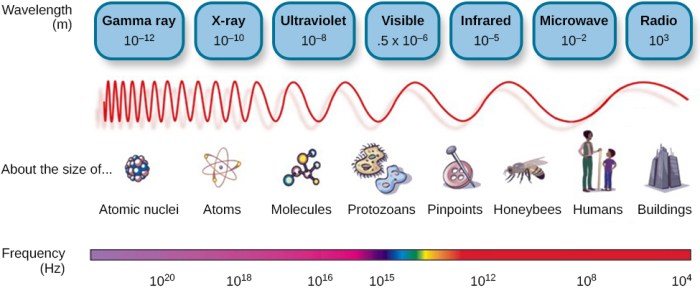
The electromagnetic spectrum is the range of all possible frequencies of electromagnetic radiation. It is divided into several regions based on frequency, including radio waves, microwaves, infrared radiation, visible light, ultraviolet radiation, X-rays, and gamma rays.
The given frequency of 6.0 falls within the radio wave region of the electromagnetic spectrum.
Wavelength and Energy
The wavelength of an electromagnetic wave is the distance between two consecutive peaks or troughs of the wave. It is inversely proportional to frequency. The energy of an electromagnetic wave is directly proportional to its frequency. The relationship between energy (E), frequency, and Planck’s constant (h) is given by the equation: E = hf.
For a frequency of 6.0 Hz, the corresponding wavelength is approximately 50 million kilometers (5 x 10^7 km).
Applications of 6.0 Frequency
Electromagnetic waves with a frequency of 6.0 Hz have various applications, including:
- Communication:Long-wave radio broadcasting (LF band)
- Medical imaging:Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
- Scientific research:Radio astronomy
Safety Considerations
Exposure to electromagnetic waves can have potential health effects, depending on the frequency and intensity of the radiation. For 6.0 Hz waves, which fall within the radio wave region, exposure is generally considered safe at low levels.
However, it is important to follow safety guidelines and avoid prolonged exposure to high-intensity electromagnetic fields, regardless of frequency.
Clarifying Questions: If The Frequency Of An Electromagnetic Wave Is 6.0
What is the significance of the frequency of an electromagnetic wave?
The frequency of an electromagnetic wave determines its position within the electromagnetic spectrum and influences its properties, such as wavelength and energy.
How is the wavelength of an electromagnetic wave related to its frequency?
Wavelength and frequency are inversely proportional. As frequency increases, wavelength decreases, and vice versa.
What are some practical applications of electromagnetic waves with a frequency of 6.0?
Electromagnetic waves with a frequency of 6.0 find applications in various fields, including communication systems, medical imaging, and scientific research.