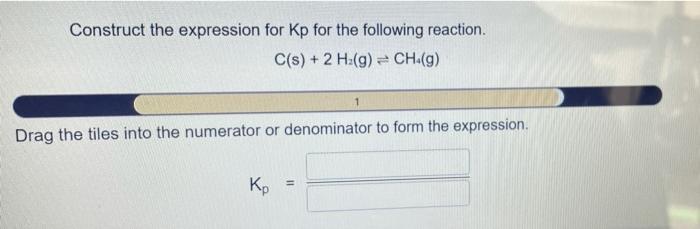
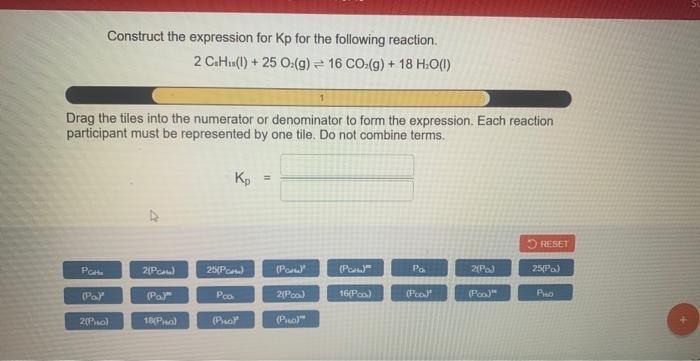
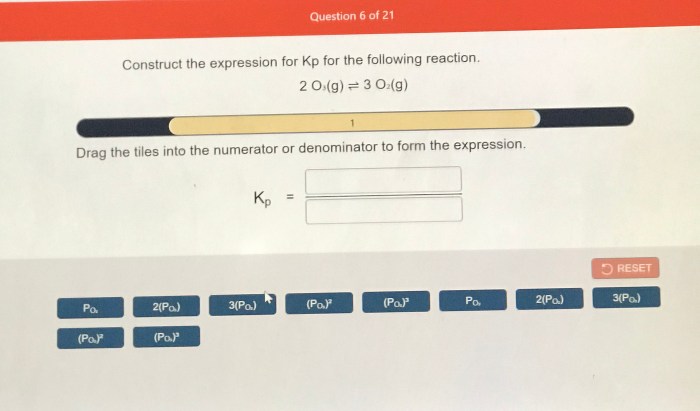
Construct the expression for kp for the following reaction. – Constructing the expression for Kp for a given reaction is a crucial step in understanding chemical equilibrium. Kp, the equilibrium constant, quantifies the extent to which a reaction proceeds towards completion and provides valuable insights into the reaction’s behavior. This comprehensive guide delves into the concept of Kp, its relationship with the extent of reaction, and the systematic approach to constructing its expression.
By identifying the reactants, products, and their stoichiometric coefficients from the balanced chemical equation, we can utilize the general expression for Kp to derive the specific expression for the given reaction. This expression serves as a powerful tool for predicting the direction of a reaction, calculating equilibrium concentrations, and gaining a deeper understanding of chemical processes.
Constructing the Expression for Kp
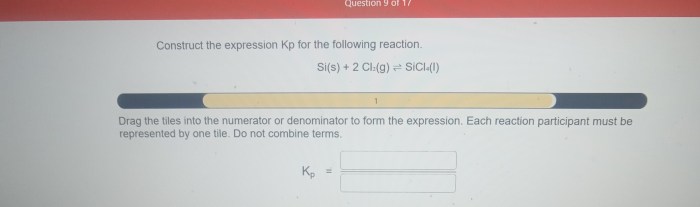
Kp is the equilibrium constant for a reaction, which is a measure of the extent to which a reaction proceeds towards completion. It is defined as the ratio of the partial pressures of the products to the partial pressures of the reactants, each raised to their respective stoichiometric coefficients.
Identifying the Reactants and Products
The first step in constructing the expression for Kp is to identify the reactants and products involved in the reaction. Reactants are the initial species that are present before the reaction occurs, while products are the final species that are formed after the reaction is complete.
Writing the Balanced Chemical Equation
Once the reactants and products have been identified, the next step is to write the balanced chemical equation for the reaction. A balanced chemical equation shows the stoichiometric coefficients of each species involved in the reaction, which are the numbers that balance the equation and ensure that the number of atoms of each element is the same on both sides of the equation.
Determining the Stoichiometric Coefficients, Construct the expression for kp for the following reaction.
The stoichiometric coefficients of each species in the balanced chemical equation are used to determine the exponents in the expression for Kp. The stoichiometric coefficient of a reactant is the number of molecules of that reactant that are consumed in the reaction, while the stoichiometric coefficient of a product is the number of molecules of that product that are formed in the reaction.
Substituting the Stoichiometric Coefficients into the General Expression for Kp
The general expression for Kp is:Kp = (P(products))^a / (P(reactants))^bwhere P(products) is the partial pressure of each product raised to its stoichiometric coefficient, P(reactants) is the partial pressure of each reactant raised to its stoichiometric coefficient, a is the sum of the stoichiometric coefficients of the products, and b is the sum of the stoichiometric coefficients of the reactants.
Popular Questions: Construct The Expression For Kp For The Following Reaction.
What is the significance of Kp in chemical reactions?
Kp provides a quantitative measure of the extent to which a reaction proceeds towards completion, allowing us to predict the direction and equilibrium concentrations of the reaction.
How does temperature affect the value of Kp?
Temperature can influence the value of Kp, with increasing temperature generally favoring reactions that absorb heat (endothermic reactions) and decreasing temperature favoring reactions that release heat (exothermic reactions).