Distance time graphs gizmo answer key – Delve into the captivating world of distance-time graphs, where the secrets of motion are unveiled through the lens of this indispensable tool. Embark on a journey to decipher the intricacies of these graphs, unraveling the mysteries of how they depict motion and empowering you to solve complex problems with unparalleled precision.
Distance-time graphs, with their seemingly simple yet profound nature, provide a powerful means to analyze and comprehend the dynamics of moving objects. Whether you’re a student seeking clarity or a seasoned professional seeking to enhance your understanding, this guide will illuminate the intricacies of distance-time graphs, empowering you to harness their full potential.
Distance-Time Graphs
Distance-time graphs are a graphical representation of the motion of an object. They show the distance traveled by an object as a function of time. The slope of a distance-time graph represents the velocity of the object.
Distance-time graphs can be used to represent a variety of types of motion, including uniform motion, accelerated motion, and decelerated motion. In uniform motion, the object moves at a constant velocity, and the distance-time graph is a straight line. In accelerated motion, the object’s velocity increases over time, and the distance-time graph is a curve that slopes upward.
In decelerated motion, the object’s velocity decreases over time, and the distance-time graph is a curve that slopes downward.
Types of Distance-Time Graphs
There are three main types of distance-time graphs:
- Linear graphs: These graphs represent objects moving with constant velocity. The slope of the graph is equal to the velocity of the object.
- Curved graphs: These graphs represent objects moving with acceleration or deceleration. The slope of the graph is changing, indicating that the velocity of the object is changing.
- Step graphs: These graphs represent objects that are moving with different velocities at different times. The graph consists of a series of horizontal and vertical line segments.
Interpreting Distance-Time Graphs

Distance-time graphs are a graphical representation of the relationship between the distance traveled by an object and the time taken to travel that distance. They can be used to determine the speed of an object, as well as to solve problems involving motion.
Slope of a Distance-Time Graph
The slope of a distance-time graph represents the speed of the object. The steeper the slope, the faster the object is moving. The slope can be calculated using the following formula:
“`slope = (change in distance) / (change in time)“`
For example, if an object travels 100 meters in 10 seconds, the slope of the distance-time graph would be 10 meters per second.
Speed of an Object
The speed of an object can be determined from a distance-time graph by finding the slope of the graph. The slope will give the speed in meters per second.
For example, if the slope of a distance-time graph is 10 meters per second, then the object is moving at a speed of 10 meters per second.
Solving Problems
Distance-time graphs can be used to solve problems involving motion. For example, they can be used to determine the distance traveled by an object in a given amount of time, or to determine the time it will take an object to travel a given distance.
To solve problems using distance-time graphs, simply follow these steps:
- Draw a distance-time graph for the object.
- Find the slope of the graph.
- Use the slope to determine the speed of the object.
- Use the speed to solve the problem.
For example, if you want to determine the distance traveled by an object in 10 seconds, simply find the slope of the distance-time graph and multiply it by 10.
Creating Distance-Time Graphs
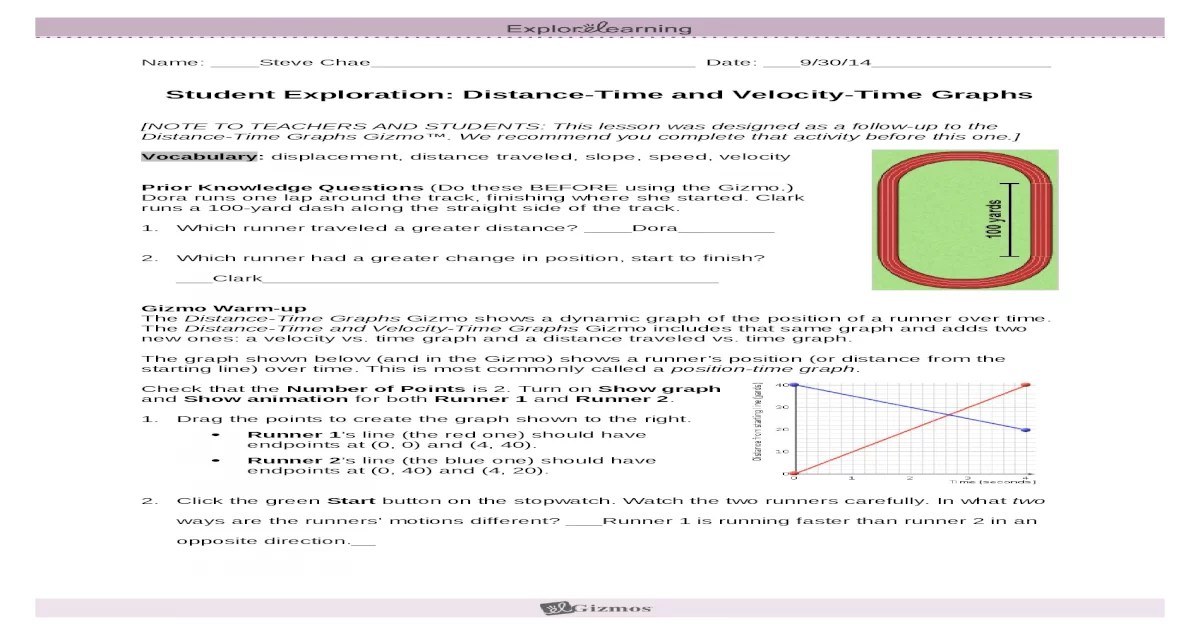
Distance-time graphs are graphical representations of the relationship between the distance traveled by an object and the time taken to travel that distance. Creating accurate and clear distance-time graphs is essential for analyzing and understanding motion.
Steps Involved in Creating a Distance-Time Graph
- Gather Data:Collect data on the distance traveled by the object at specific time intervals.
- Choose Scales:Select appropriate scales for the horizontal (time) and vertical (distance) axes. The scales should be chosen to ensure that the graph is clear and easy to read.
- Plot Data Points:Plot the data points on the graph, with the time values on the horizontal axis and the distance values on the vertical axis.
- Draw the Graph:Connect the data points with a line or curve to represent the relationship between distance and time.
Choosing Appropriate Scales
Choosing appropriate scales is crucial for creating a clear and informative graph. The scales should be chosen so that:
- The entire graph fits comfortably within the available space.
- The data points are spread out enough to be easily distinguishable.
- The axes are labeled clearly and accurately.
Tips for Creating Clear and Accurate Distance-Time Graphs
- Use a ruler or graph paper to ensure accuracy.
- Label the axes clearly with the appropriate units.
- Draw a smooth line or curve that best represents the data points.
- Add a title to the graph that describes the motion being represented.
Applications of Distance-Time Graphs
Distance-time graphs are versatile tools used in various fields to analyze and represent motion. They provide a graphical representation of the relationship between distance and time, enabling researchers and practitioners to understand the movement patterns of objects.
Science
In science, distance-time graphs are used to:
- Study projectile motion:Analyze the trajectory and velocity of projectiles, such as rockets or missiles.
- Determine acceleration:Calculate the rate of change in velocity over time, providing insights into the forces acting on an object.
- Investigate motion in fluids:Understand the movement of objects through liquids or gases, such as the flow of water in pipes or the flight of birds.
Engineering
In engineering, distance-time graphs are employed to:
- Design vehicle trajectories:Plan the movement of vehicles, such as cars, trains, and airplanes, to optimize speed and efficiency.
- Control robotic systems:Program robots to move precisely and efficiently by analyzing distance-time graphs to determine optimal paths.
li> Analyze traffic patterns:Study the flow of traffic on roads and highways, identifying congestion points and potential improvements.
Everyday Life
In everyday life, distance-time graphs have practical applications in:
- Planning travel routes:Determine the distance and travel time for different routes, enabling efficient planning of journeys.
- Monitoring fitness:Track distance covered and speed during exercise, providing insights into performance and progress.
- Analyzing sports performance:Evaluate the movement patterns of athletes, such as runners or cyclists, to identify areas for improvement.
Limitations and Alternatives, Distance time graphs gizmo answer key
While distance-time graphs are valuable tools, they have certain limitations:
- Limited to one-dimensional motion:They cannot represent movement in multiple dimensions.
- May not capture all aspects of motion:They do not provide information about velocity, acceleration, or forces.
Alternative methods for representing motion include:
- Velocity-time graphs:Show the velocity of an object over time.
- Acceleration-time graphs:Display the acceleration of an object over time.
- Position-velocity-acceleration graphs:Provide a comprehensive representation of an object’s motion, including position, velocity, and acceleration.
The choice of representation depends on the specific application and the desired information.
Quick FAQs: Distance Time Graphs Gizmo Answer Key
What are distance-time graphs?
Distance-time graphs are graphical representations of an object’s motion, plotting the distance traveled by the object on the vertical axis against the time elapsed on the horizontal axis.
How can I interpret the slope of a distance-time graph?
The slope of a distance-time graph represents the object’s velocity, or the rate at which the object is moving.
How can I use distance-time graphs to solve problems?
Distance-time graphs can be used to determine an object’s displacement, velocity, acceleration, and other motion-related parameters.

